
Sacred Texts Taoism Index Previous Next

1. Zeh-yang having travelled to Khû, Î Kieh 2 spoke of him to the king, and then, before the king had granted him an interview, (left him, and) returned home. Zeh-yang went to see Wang Kwo 3, and said to him, 'Master, why do you not mention me to the king?' Wang Kwo replied, 'I am not so good a person to do that as Kung-yüeh Hsiû 4.' 'What sort of man is he?' asked the other, and the reply was, 'In winter he spears turtles in the Kiang, and in summer he rests in shady places on the mountain. When passers-by ask him (what he is doing there), he says, "This is my abode." Since Î Kieh was not able to induce the king to see you, how much less should I, who am not equal to him, be able to do so! Î Kieh's character is this:--he has no (real) virtue, but he has knowledge. If you do not freely yield yourself to him, but employ him to carry on his spirit-like influence (with you), you will certainly get upset and benighted in the region of riches and honours. His help will not be of a virtuous character, but will go to make your virtue
less;--it will be like heaping on clothes in spring as a protection against cold, or bringing back the cold winds of winter as a protection against heat (in summer). Now the king of Khû is of a domineering presence and stern. He has no forgiveness for offenders, but is merciless as a tiger. It is only a man of subtle speech, or one of correct virtue, who can bend him from his purpose 1.
'But the sagely man 2, when he is left in obscurity, causes the members of his family to forget their poverty; and, when he gets forward to a position of influence, causes kings and dukes to forget their rank and emoluments, and transforms them to be humble. With the inferior creatures, he shares their pleasures, and they enjoy themselves the more; with other men, he rejoices in the fellowship of the Tâo, and preserves it in himself. Therefore though he may not speak, he gives them to drink of the harmony (of his spirit). Standing in association with them, he transforms them till they become in their feeling towards him as sons with a father. His wish is to return to the solitude of his own mind, and this is the effect of his occasional intercourse with them. So far-reaching is his influence on the minds of men; and therefore I said to you. "Wait for Kung-yüeh Hsiû.'''
2. The sage comprehends the connexions between himself and others, and how they all go to constitute him of one body with them, and he does not know how it is so;--he naturally does so. In fulfilling his constitution, as acted on and acting, he
[paragraph continues] (simply) follows the direction of Heaven; and it is in consequence of this that men style him (a sage). If he were troubled about (the insufficiency of) his knowledge, what he did would always be but small, and sometimes would be arrested altogether;--how would he in this case be (the sage)? When (the sage) is born with all his excellence, it is other men who see it for him. If they did not tell him, he would not know that he was more excellent than others. And when he knows it, he is as if he did not know it; when he hears it, he is as if he did not hear it. His source of joy in it has no end, and men's admiration of him has no end;--all this takes place naturally 1. The love of the sage for others receives its name from them. If they did not tell him of it, he would not know that he loved them; and when he knows it, he is as if he knew it not; when he hears it, he is as if he heard it not. His love of others never has an end, and their rest in him has also no end:--all this takes place naturally 1.
3. When one sees at a distance his old country and old city, he feels a joyous satisfaction 2. Though it be full of mounds and an overgrowth of trees and grass, and when he enters it he finds but a tenth part remaining, still he feels that satisfaction. How much more when he sees what he saw, and hears what he heard before! All this is to him like a tower eighty cubits high exhibited in the sight of all men.
(The sovereign) Zän-hsiang 1 was possessed of that central principle round which all things revolve 2, and by it he could follow them to their completion. His accompanying them had neither ending nor beginning, and was independent of impulse or time. Daily he witnessed their changes, and himself underwent no change; and why should he not have rested in this? If we (try to) adopt Heaven as our Master, we incapacitate ourselves from doing so. Such endeavour brings us under the power of things. If one acts in this way, what is to be said of him? The sage never thinks of Heaven nor of men. He does not think of taking the initiative, nor of anything external to himself. He moves along with his age, and does not vary or fail. Amid all the completeness of his doings, he is never exhausted. For those who wish to be in accord with him, what other course is there to pursue?
When Thang got one to hold for him the reins of government, namely, Män-yin Täng-häng 3, he employed him as his teacher. He followed his master, but did not allow himself to be hampered by him, and so he succeeded in following things to their completion. The master had the name; but that name was a superfluous addition to his laws, and the twofold character of his government was made apparent 4. Kung-nî's 'Task your thoughts to the utmost' was his expression of the duties of a
master. Yung-khäng said, 'Take the days away and there will be no year; without what is internal there will be nothing external 1.'
4. (King) Yung 2 of Wei made a treaty with the marquis Thien Mâu 3 (of Khî), which the latter violated. The king was enraged, and intended to send a man to assassinate him. When the Minister of War 4 heard of it, he was ashamed, and said (to the king), 'You are a ruler of 10,000 chariots, and by means of a common man would avenge yourself on your enemy. I beg you to give me, Yen, the command of 200,000 soldiers to attack him for you. I will take captive his people and officers, halter (and lead off) his oxen and horses, kindling a fire within him that shall burn to his backbone. I will then storm his capital; and when he shall run away in terror, I will flog his back and break his spine.' Kî-dze 5 heard of this advice, and was ashamed of it, and said (to the king), 'We have been raising the wall (of our capital) to a height of eighty cubits, and the work has been completed. If we now get it thrown down, it will be a painful toil to the convict builders. It is now seven years
since our troops were called out, and this is the foundation of the royal sway. Yen would introduce disorder;--he should not be listened to.' Hwâ-dze 1 heard of this advice, and, greatly disapproving of it, said (to the king), 'He who shows his skill in saying "Attack Khî" would produce disorder; and he who shows his skill in saying "Do not attack it" would also produce disorder. And one who should (merely) say, "The counsellors to attack Khî and not to attack it would both produce disorder," would himself also lead to the same result.' The king said, 'Yes, but what am I to do?' The reply was, 'You have only to seek for (the rule of) the Tâo (on the subject).'
Hui-dze, having heard of this counsel, introduced to the king Tâi Zin-zän 2, who said, 'There is the creature called a snail; does your majesty know it?' 'I do.' 'On the left horn of the snail there is a kingdom which is called Provocation, and on the right horn another which is called Stupidity. These two kingdoms are continually striving about their territories and fighting. The corpses that lie on the ground amount to several myriads. The army of one may be defeated and put to flight, but in fifteen days it will return.' The king said, 'Pooh! that is empty talk!' The other rejoined, 'Your servant begs to show your majesty its real significance. When your majesty thinks of space--east, west, north, and south, above and beneath--can you set any limit to it?' 'It is illimitable,' said the king; and his visitor went on, 'Your majesty knows
how to let your mind thus travel through the illimitable, and yet (as compared with this) does it not seem insignificant whether the kingdoms that communicate one with another exist or not?' The king replies, 'It does so;' and Tâi Zin-zän said, finally, 'Among those kingdoms, stretching one after another, there is this Wei; in Wei there is this (city of) Liang 1; and in Liang there is your majesty. Can you make any distinction between yourself, and (the king of that kingdom of) Stupidity?' To this the king answered, 'There is no distinction,' and his visitor went out, while the king remained disconcerted and seemed to have lost himself.
When the visitor was gone, Hui-dze came in and saw the king, who said, 'That stranger is a Great man. An (ordinary) sage is not equal to him.' Hui-dze replied, 'If you blow into a flute, there come out its pleasant notes; if you blow into a sword-hilt, there is nothing but a wheezing sound. Yâo and Shun are the subjects of men's praises, but if you speak of them before Tai Zin-zän, there will be but the wheezing sound.'
5. Confucius, having gone to Khû, was lodging in the house of a seller of Congee at Ant-hill. On the roof of a neighbouring house there appeared the husband and his wife, with their servants, male and female 2. Dze-lû said, 'What are those people doing,
collected there as we see them?' Kung-nî replied, 'The man is a disciple of the sages. He is burying himself among the people, and hiding among the fields. Reputation has become little in his eyes, but there is no bound to his cherished aims. Though he may speak with his mouth, he never tells what is in his mind. Moreover, he is at variance with the age, and his mind disdains to associate with it;--he is one who may be said to lie hid at the bottom of the water on the dry land. Is he not a sort of Î Liâo of Shih-nan?' Dze-lû asked leave to go and call him, but Confucius said, 'Stop. He knows that I understand him well. He knows that I am come to Khû, and thinks that I am sure to try and get the king to invite him (to court). He also thinks that I am a man swift to speak. Being such a man, he would feel ashamed to listen to the words of one of voluble and flattering tongue, and how much more to come himself and see his person! And why should we think that he will remain here?' Dze-lû, however, went to see how it was, but found the house empty.
6. The Border-warden of Khang-wû 1, in questioning Dze-lâo 2, said, 'Let not a ruler in the exercise of his government be (like the farmer) who leaves the clods unbroken, nor, in regulating his people, (like one) who recklessly plucks up the shoots. Formerly, in ploughing my corn-fields, I left the clods unbroken, and my recompense was in the rough unsatisfactory crops; and in weeding, I destroyed and tore up (many good plants), and my recompense was in the scantiness of my harvests. In subsequent
years I changed my methods, ploughing deeply and carefully covering up the seed; and my harvests were rich and abundant, so that all the year I had more than I could eat.' When Kwang-dze heard of his remarks, he said, 'Now-a-days, most men, in attending to their bodies and regulating their minds, correspond to the description of the Border-warden. They hide from themselves their Heaven(-given being); they leave (all care of) their (proper) nature; they extinguish their (proper) feelings; and they leave their spirit to die:--abandoning themselves to what is the general practice. Thus dealing with their nature like the farmer who is negligent of the clods in his soil, the illegitimate results of their likings and dislikings become their nature. The bushy sedges, reeds, and rushes, which seem at first to spring up to support our bodies, gradually eradicate our nature, and it becomes like a mass of running sores, ever liable to flow out, with scabs and ulcers, discharging in flowing matter from the internal heat. So indeed it is!'
7. Po Kü 1 was studying with Lâo Tan, and asked his leave to go and travel everywhere. Lao Tan said, 'Nay;--elsewhere it is just as here.' He repeated his request, and then Lâo Tan said, 'Where would you go first?' 'I would begin with Khî,' replied the disciple. Having got there, I would go to look at the criminals (who had been executed). With my arms I would raise (one of) them up and set him on his feet, and, taking off my court robes, I would cover him with them, appealing at
the same time to Heaven and bewailing his lot, while I said 1, "My son, my son, you have been one of the first to suffer from the great calamities that afflict the world 2."' (Lâo Tan) said 1, '(It is said), ---Do not rob. Do not kill." (But) in the setting up of (the ideas of) glory and disgrace, we see the cause of those evils; in the accumulation of property and wealth, we see the causes of strife and contention. If now you set up the things against which men fret; if you accumulate what produces strife and contention among them; if you put their persons in such a state of distress, that they have no rest or ease, although you may wish that they should not come to the end of those (criminals), can your wish be realised?
'The superior men (and rulers) of old considered that the success (of their government) was to be found in (the state of) the people, and its failure to be sought in themselves; that the right might be with the people, and the wrong in themselves. Thus it was that if but a single person lost his life, they retired and blamed themselves. Now, however, it is not so. (Rulers) conceal what they want done, and hold those who do not know it to be stupid; they require what is very difficult, and condemn those who do not dare to undertake it; they impose heavy burdens, and punish those who are unequal to them; they require men to go far, and put them to death when they cannot accomplish the distance. When the people know that the utmost of their
strength will be insufficient, they follow it up with deceit. When (the rulers) daily exhibit much hypocrisy, how can the officers and people not be hypocritical? Insufficiency of strength produces hypocrisy; insufficiency of knowledge produces deception; insufficiency of means produces robbery. But in this case against whom ought the robbery and theft to be charged?'
8. When Kü Po-yü was in his sixtieth year, his views became changed in the course of it 1. He had never before done anything but consider the views which he held to be right, but now he came to condemn them as wrong; he did not know that what he now called right was not what for fifty-nine years he had been calling wrong. All things have the life (which we know), but we do not see its root; they have their goings forth, but we do not know the door by which they depart. Men all honour that which lies within the sphere of their knowledge, but they do not know their dependence on what lies without that sphere which would be their (true) knowledge:--may we not call their case one of great perplexity? Ah! Ah! there is no escaping from this dilemma. So it is! So it is!
9. Kung-nî asked the Grand Historiographer 2 Tâ Thâo, (along with) Po Khang-khien and Khih-wei, saying, 'Duke Ling of Wei was so addicted to
drink, and abandoned to sensuality, that he did not attend to the government of his state. Occupied in his pursuit of hunting with his nets and bows, he kept aloof from the meetings of the princes. In what was it that he showed his title to the epithet of Ling 1?' Tâ Thâo said, 'It was on account of those very things.' Po Khang-khien said, 'Duke Ling had three mistresses with whom he used to bathe in the same tub. (Once, however), when Shih-zhiû came to him with presents from the imperial court, he made his servants support the messenger in bearing the gifts 2. So dissolute was he in the former case, and when he saw a man of worth, thus reverent was he to him. It was on this account that he was styled "Duke Ling." Khih-wei said, 'When duke Ling died, and they divined about burying him in the old tomb of his House, the answer was unfavourable; when they divined about burying him on Shâ-khiû, the answer was favourable. Accordingly they dug there to the depth of several fathoms, and found a stone coffin. Having washed and inspected it, they discovered an inscription, which said,
"This grave will not be available for your posterity;
Duke Ling will appropriate it for himself."
Thus that epithet of Ling had long been settled for the duke 1. But how should those two be able to know this
10. Shâo Kih 2 asked Thâi-kung Thiâo 2, saying, 'What do we mean by "The Talk of the Hamlets and Villages?" The reply was, 'Hamlets and Villages are formed by the union--say of ten surnames and a hundred names, and are considered to be (the source of) manners and customs. The differences between them are united to form their common character, and what is common to them is separately apportioned to form the differences. If you point to the various parts which make up the body of a horse, you do not have the horse; but when the horse is before you, and all its various parts stand forth (as forming the animal), you speak of "the horse." So it is that the mounds and hills are made to be the elevations that they are by accumulations of earth which individually are but low. (So also rivers like) the Kiang and the Ho obtain their greatness by the union of (other smaller) waters with them. And (in the same way) the Great man exhibits the common sentiment of humanity by the union in himself of all its individualities. Hence when ideas come to him from without, though he
has his own decided view, he does not hold it with bigotry; and when he gives out his own decisions, which are correct, the views of others do not oppose them. The four seasons have their different elemental characters, but they are not the partial gifts of Heaven, and so the year completes its course. The five official departments have their different duties, but the ruler does not partially employ any one of them, and so the kingdom is governed. (The gifts of) peace and war(are different), but the Great man does not employ the one to the prejudice of the other, and so the character (of his administration) is perfect. All things have their different constitutions and modes of actions, but the Tâo (which directs them) is free from all partiality, and therefore it has no name. Having no name, it therefore does nothing. Doing nothing, there is nothing which it does not do.
'Each season has its ending and beginning; each age has its changes and transformations; misery and happiness regularly alternate. Here our views are thwarted, and yet the result may afterwards have our approval; there we insist on our own views, and looking at things differently from others, try to correct them, while we are in error ourselves. The case may be compared to that of a great marsh, in which all its various vegetation finds a place, or we may look at it as a great hill, where trees and rocks are found on the same terrace. Such may be a description of what is intended by "The Talk of the Hamlets and Villages."'
Shâo Kih said, 'Well, is it sufficient to call it (an expression of) the Tâo?' Thâi-kung Thiâo said, 'It is not so. If we reckon up the number of things,
they are not 10,000 merely. When we speak of them as "the Myriad Things," we simply use that large number by way of accommodation to denominate them. In this way Heaven and Earth are the greatest of all things that have form; the Yin and Yang are the greatest of all elemental forces. But the Tâo is common to them. Because of their greatness to use the Tâo or (Course) as a title and call it "the Great Tâo" is allowable. But what comparison can be drawn between it and "the Talk of the Hamlets and Villages?" To argue from this that it is a sufficient expression of the Tâo, is like calling a dog and a horse by the same name, while the difference between them is so great.'
11. Shâo Kih said, 'Within the limits of the four cardinal points, and the six boundaries of space, how was it that there commenced the production of all things?' Thâi-kung Thiâo replied, 'The Yin and Yang reflected light on each other, covered each other, and regulated each the other; the four seasons gave place to one another, produced one another, and brought one another to an end. Likings and dislikings, the avoidings of this and movements towards that, then arose (in the things thus produced), in their definite distinctness; and from this came the separation and union of the male and female. Then were seen now security and now insecurity, in mutual change; misery and happiness produced each other; gentleness and urgency pressed on each other; the movements of collection and dispersion were established:--these names and processes can be examined, and, however minute, can be recorded. The rules determining the order in which they follow one another, their mutual influence
now acting directly and now revolving, how, when they are exhausted, they revive, and how they end and begin again; these are the properties belonging to things. Words can describe them and knowledge can reach to them; but with this ends all that can be said of things. Men who study the Tâo do not follow on when these operations end, nor try to search out how they began:--with this all discussion of them stops.'
Shâo Kih said, 'Kî Kän 1 holds that (the Tâo) forbids all action, and Kieh-dze 1 holds that it may perhaps allow of influence. Which of the two is correct in his statements, and which is one-sided in his ruling?' Thâi-kung Thiâo replied, 'Cocks crow and dogs bark;--this is what all men know. But men with the greatest wisdom cannot describe in words whence it is that they are formed (with such different voices), nor can they find out by thinking what they wish to do. We may refine on this small point; till it is so minute that there is no point to operate on, or it may become so great that there is no embracing it. "Some one caused it;" "No one did it;" but we are thus debating about things; and the end is that we shall find we are in error. "Some one caused it;"--then there was a real Being. "No one did it;"--then there was mere vacancy. To have a name and a real existence,-that is the condition of a thing. Not to have a name, and not
to have real being;--that is vacancy and no thing. We may speak and we may think about it, but the more we speak, the wider shall we be of the mark. Birth, before it comes, cannot be prevented; death, when it has happened, cannot be traced farther. Death and life are not far apart; but why they have taken place cannot be seen. That some one has caused them, or that there has been no action in the case are but speculations of doubt. When I look for their origin, it goes back into infinity; when I look for their end, it proceeds without termination. Infinite, unceasing, there is no room for words about (the Tâo). To regard it as in the category of things is the origin of the language that it is caused or that it is the result of doing nothing; but it would end as it began with things. The Tâo cannot have a (real) existence; if it has, it cannot be made to appear as if it had not. The name Tâo is a metaphor, used for the purpose of description 1. To say that it causes or does nothing is but to speak of one phase of things, and has nothing to do with the Great Subject. If words were sufficient for the purpose, in a day's time we might exhaust it; since they are not sufficient, we may speak all day, and only exhaust (the subject of) things. The Tâo is the extreme to which things conduct us. Neither speech nor silence is sufficient to convey the notion of it. Neither by speech nor by silence can our thoughts about it have their highest expression.
114:1 See vol. xxxix, pp. 154, 155.
114:2 A native of Khû, and, probably, a parasite of the court.
114:3 An officer of Khû, 'a worthy man.'
114:4 A recluse of Khû, but not keeping quite aloof from the court.
115:1 Much of the description of Î Kieh is difficult to construe.
115:2 Kung-yüeh Hsiû.
116:1 That is, 'he does so in the spontaneity of his nature.' The
 requires the employment of the term 'nature' here, not according to any abstract usage of the term, but meaning the natural constitution. Compare the
requires the employment of the term 'nature' here, not according to any abstract usage of the term, but meaning the natural constitution. Compare the
 in Mencius VII. i, 30.
in Mencius VII. i, 30.
116:2 So does he rejoice in attaining to the knowledge of his nature.
117:1 A sage sovereign prior to the three Hwang or August ones.
117:2 See the same phraseology in Book II, par. 3.
117:3 I have followed Lin Hsî-hung in taking these four characters as the name of one man.
117:4 There was a human element in it instead of the Heavenly only; but some critics think the text here is erroneous or defective.
118:1 Said to have been employed by Hwang-Tî to make the calendar.
118:2 B.C. 370-317.
118:3 I do not find the name Mâu as belonging to any of the Thien rulers of Khî. The name of the successor of Thien Ho, who has been before us, was
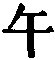 , Wû, for which
, Wû, for which
 , Mâu, may be a mistake; or 'the marquis Mâu' may be a creation of our author.
, Mâu, may be a mistake; or 'the marquis Mâu' may be a creation of our author.
118:4 Literally, 'the Rhinoceros' Head,' the title of 'the Minister of War' in Wei, who was at this time a Kung-sun Yen. See the memoir of him in Sze-mâ Khien, Book IX. of his Biographies.
118:5 I do not know that anything more can be said of Kî and Hwâ than that they were officers of Wei.
119:1 See note 5 on preceding page.
119:2 Evidently a man of considerable reach of thought.
120:1 Liang, the capital, came to be used also as the name of the state;--as in Mencius.
120:2 'They were on the roof, 'repairing it' say some. 'They had got on the roof, to get out of the way of Confucius,' say others. The sequel shows that this second interpretation is correct; but we do not see how the taking to the roof facilitated their departure from the house.
121:1 Probably the same as the Khang-Wû Dze in Book II, par. 9.
121:2 See Analects IX, vi, 4.
122:1 We can only say of Po Kü that he was a disciple of Lâo-dze.
123:1 There are two
 here, and the difficulty in translating is to determine the subject of each.
here, and the difficulty in translating is to determine the subject of each.
123:2 The
 of the text here is taken as =
of the text here is taken as =
 .
.
124:1 Confucius thought highly of this Kü Po-yü, and they were friends (Analects, XIV, 26; XV, 6). It would seem from this paragraph that, in his sixtieth year, he adopted the principles of Tâoism. Whether he really did so we cannot tell. See also Book IV, par. 5.
124:2 We must translate here in the singular, for in the historiographer's department there were only two officers with the title of 'Grand;' Po Khang-khien and Khih-wei would be inferior members of it.
125:1 Ling (
 ) as a posthumous epithet, has various meanings, none of them very bad, and some of them very good. Confucius ought to have been able to solve his question himself better than any of the historiographers, but he propounded his doubt to them for reasons which he, no doubt, had.
) as a posthumous epithet, has various meanings, none of them very bad, and some of them very good. Confucius ought to have been able to solve his question himself better than any of the historiographers, but he propounded his doubt to them for reasons which he, no doubt, had.
125:2 We are not to suppose that the royal messenger found him in the tub with his three wives or mistresses. The two incidents mentioned illustrate two different phases of his character, as some of the critics, and even the text itself, clearly indicate.
126:1 This explanation is, of course, absurd.
126:2 These two names are both metaphorical, the former meaning 'Small Knowledge,' and the latter, 'The Grand Public and just Harmonizer.' Small Knowledge would look for the Tâo in the ordinary talk of ordinary men. The other teaches him that it is to be found in 'the Great man,' blending in himself what is 'just' in the sentiments and practice of all men. And so it is to be found in all the phenomena of nature, but it has itself no name, and does nothing.
129:1 Two masters of schools of Tâoism. Who the former was I do not know; but Sze-mâ Khien in the seventy-fourth Book of his Records mentions several Tâoist masters, and among them Kieh-dze, a native of Khî, 'a student of the arts of the Tâo and its Characteristics, as taught by Hwang-Tî and Lâo-dze, and who also published his views on the subject.'
130:1 A very important statement with regard to the meaning of the name Tâo.